New Dimensions in High-Entropy Field: High-Entropy Alloy Fibers
-
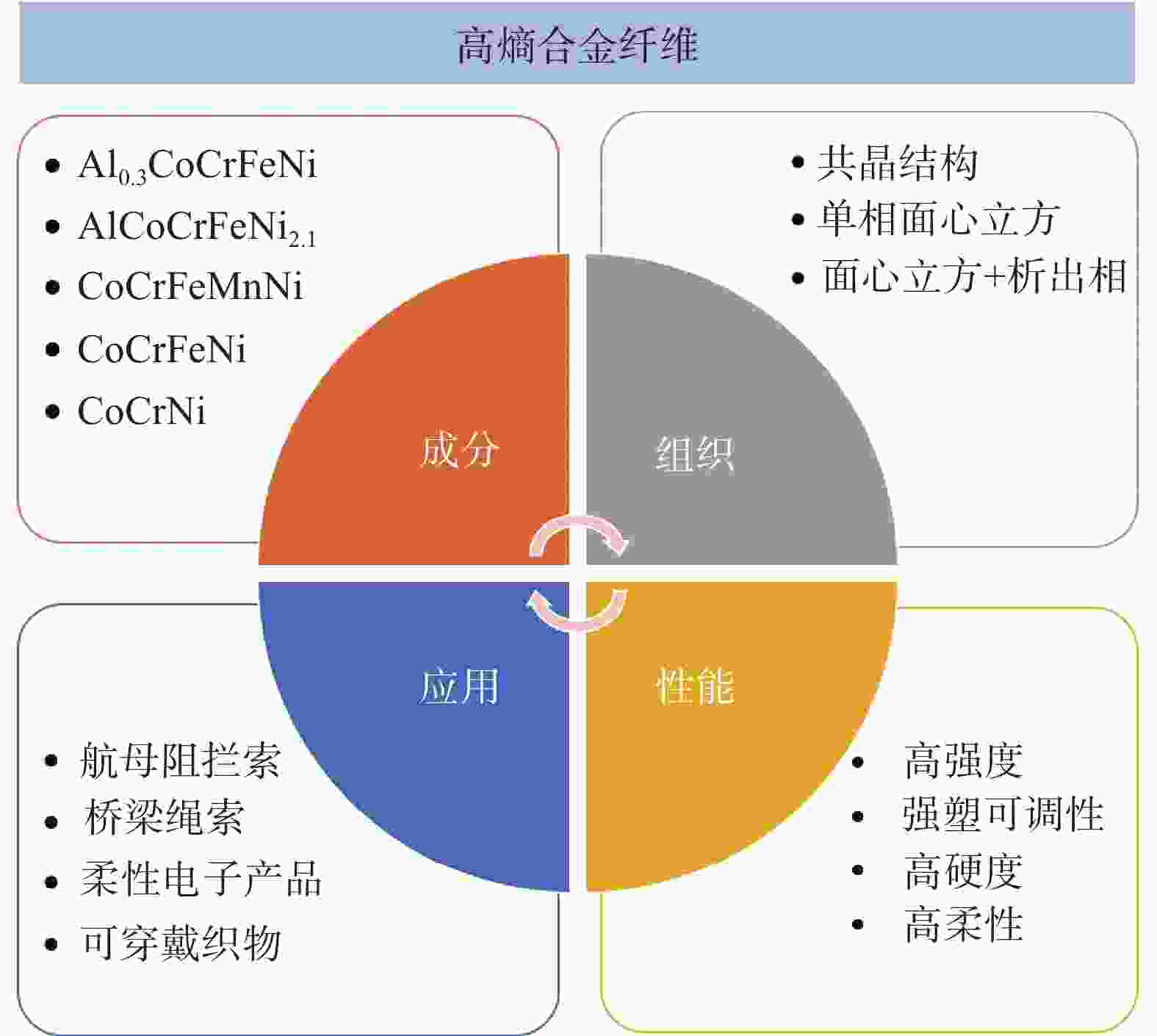
摘要: 本文聚焦于探索高熵合金纤维在材料领域的全新视角,特别关注其在柔性材料领域潜在的应用。通过对高熵合金纤维的多元性、材料特性和性能可调性进行深入研究,揭示了其在构建新一代柔性材料方面所具备的巨大潜力。着眼于从一维角度出发,使得高熵合金纤维与传统的三维块体或二维薄膜截然不同,为高熵合金带来了全新的视野和可能性。
-
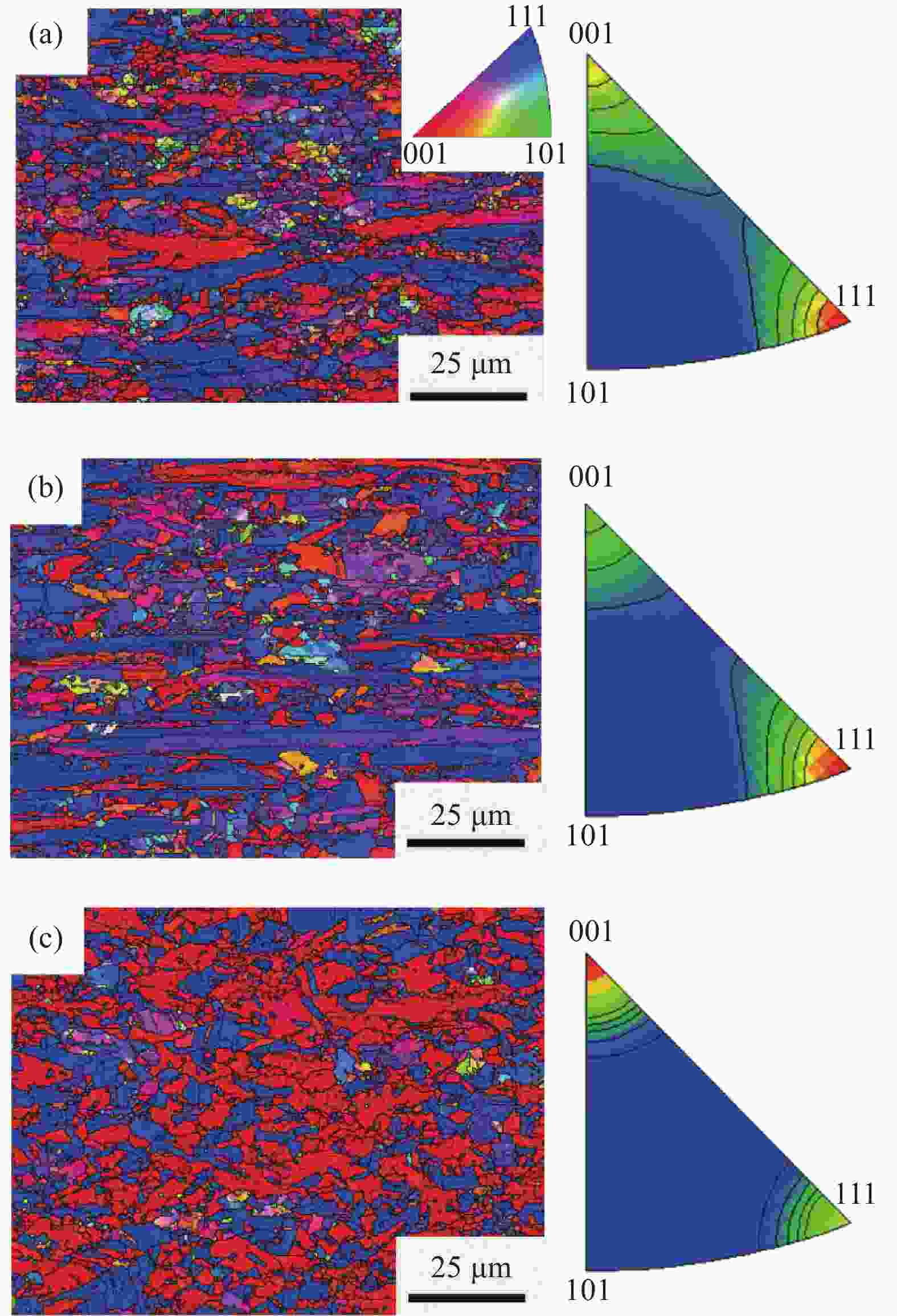
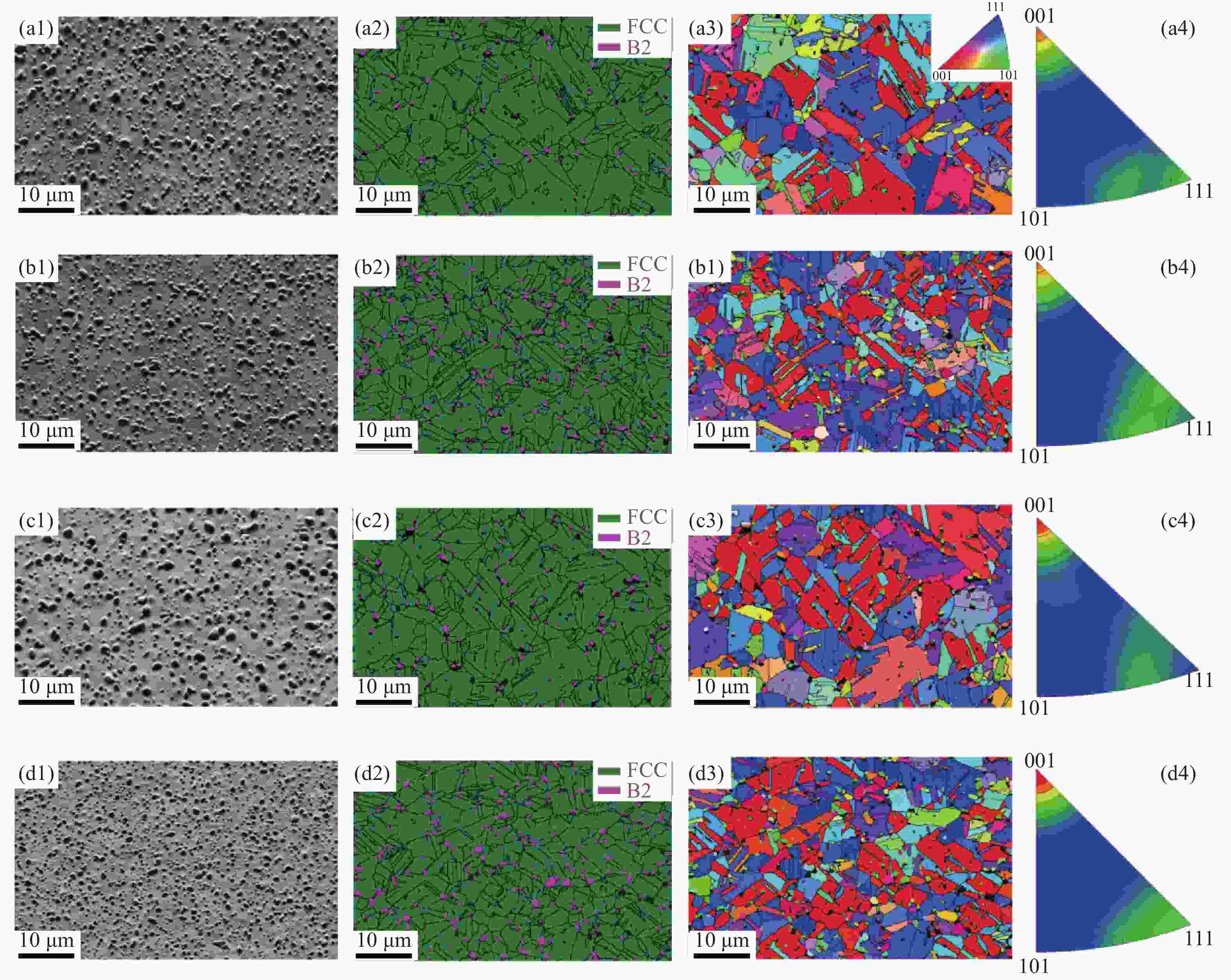
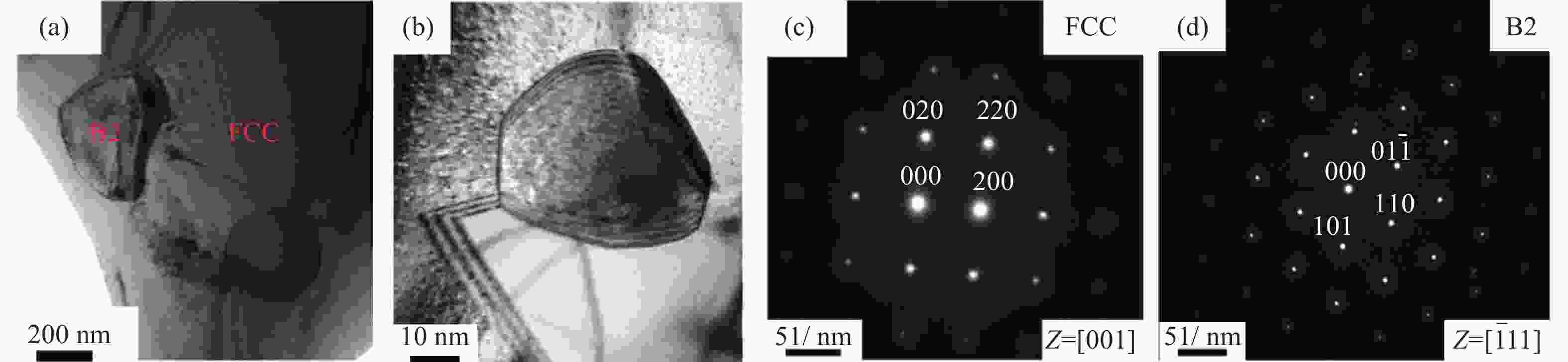
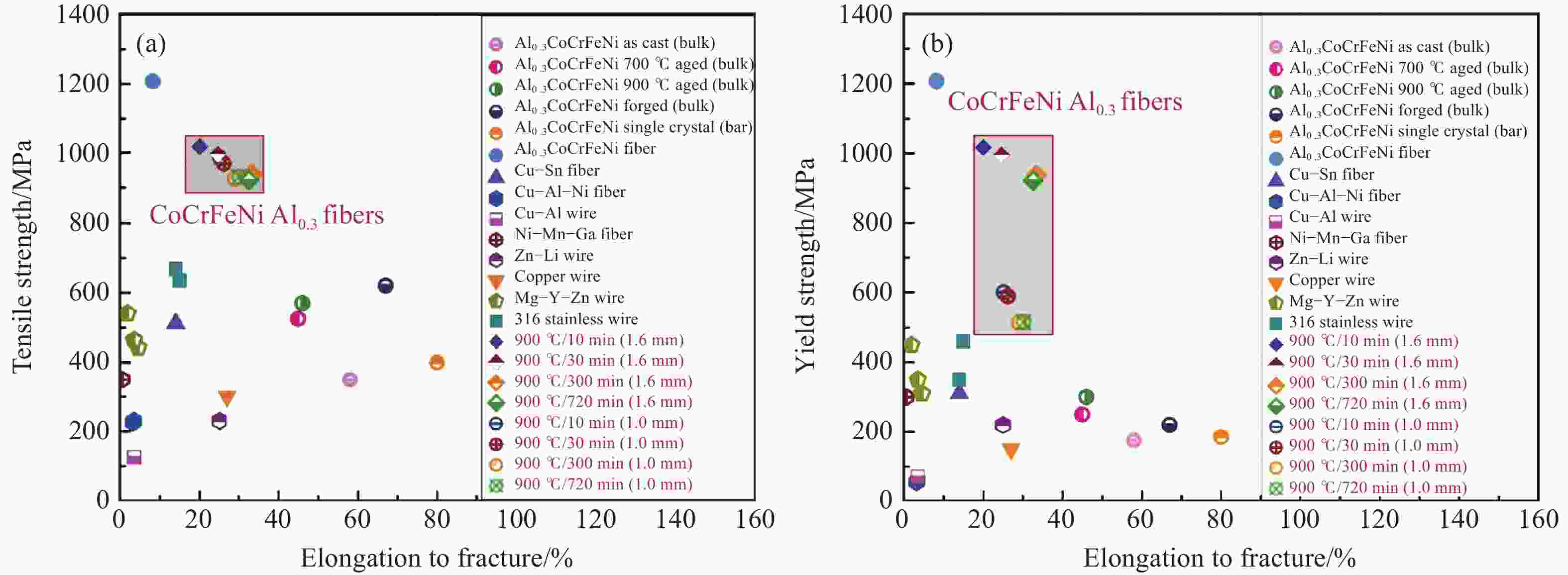
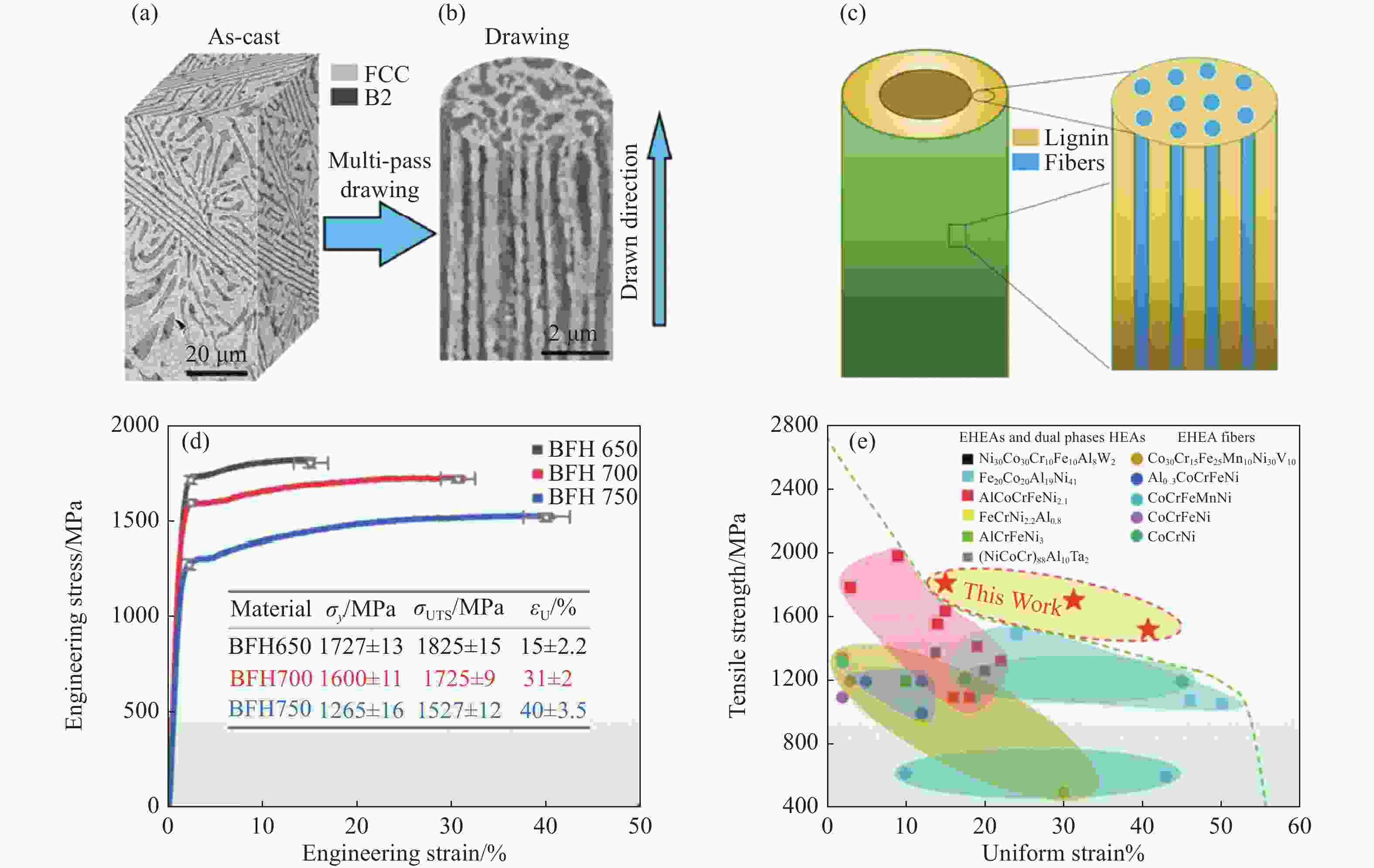
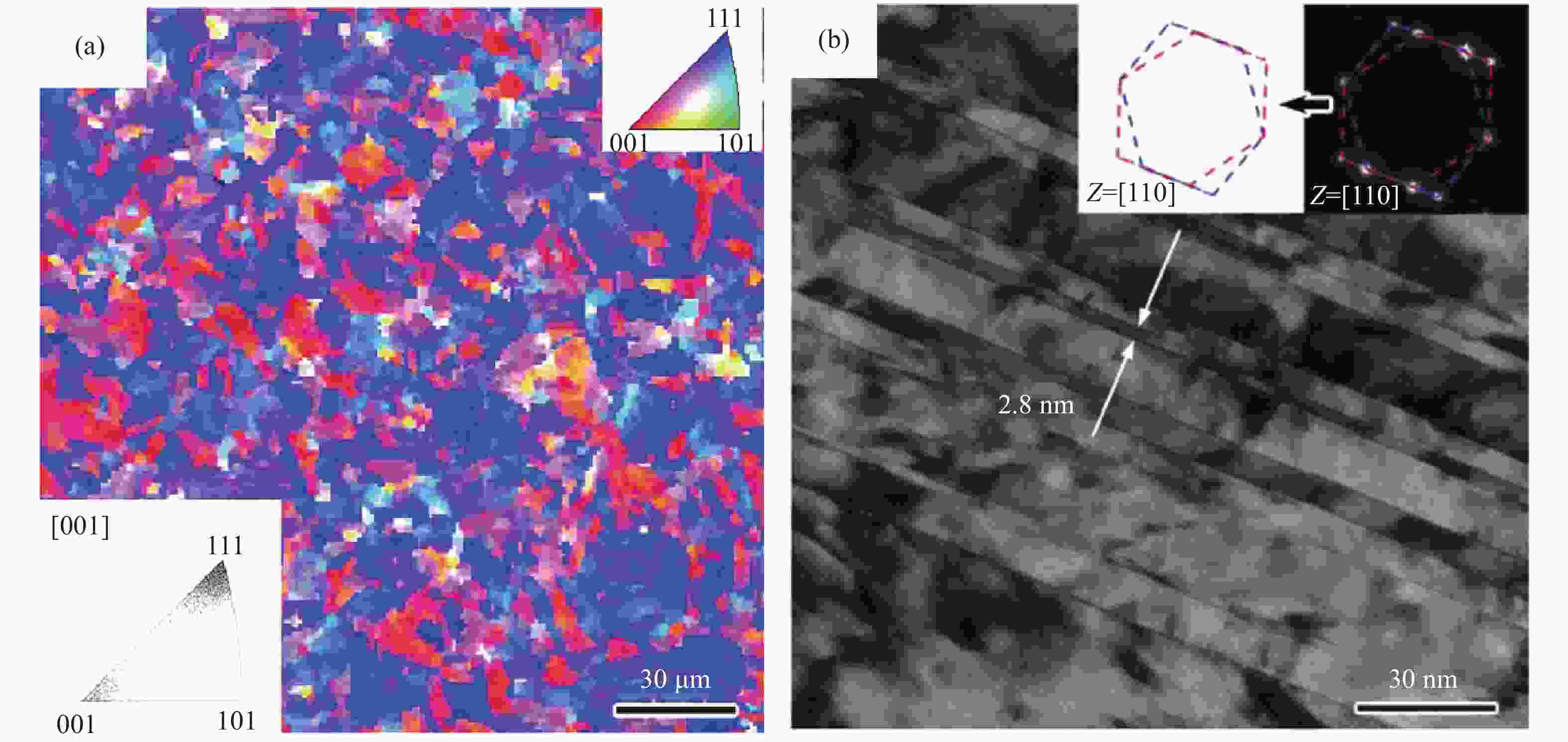
图 8 AlCoCrFeNi2.1共晶高熵合金纤维:(a) 铸态样品背散射电子图像;(b)高熵合金纤维的背散射电子图像;(c)纤维微观结构示意图;(d) 高熵合金纤维工程应力–应变曲线;(e) AlCoCrFeNi2.1高熵合金纤维与其他高熵合金纤维的力学性能对比[32]
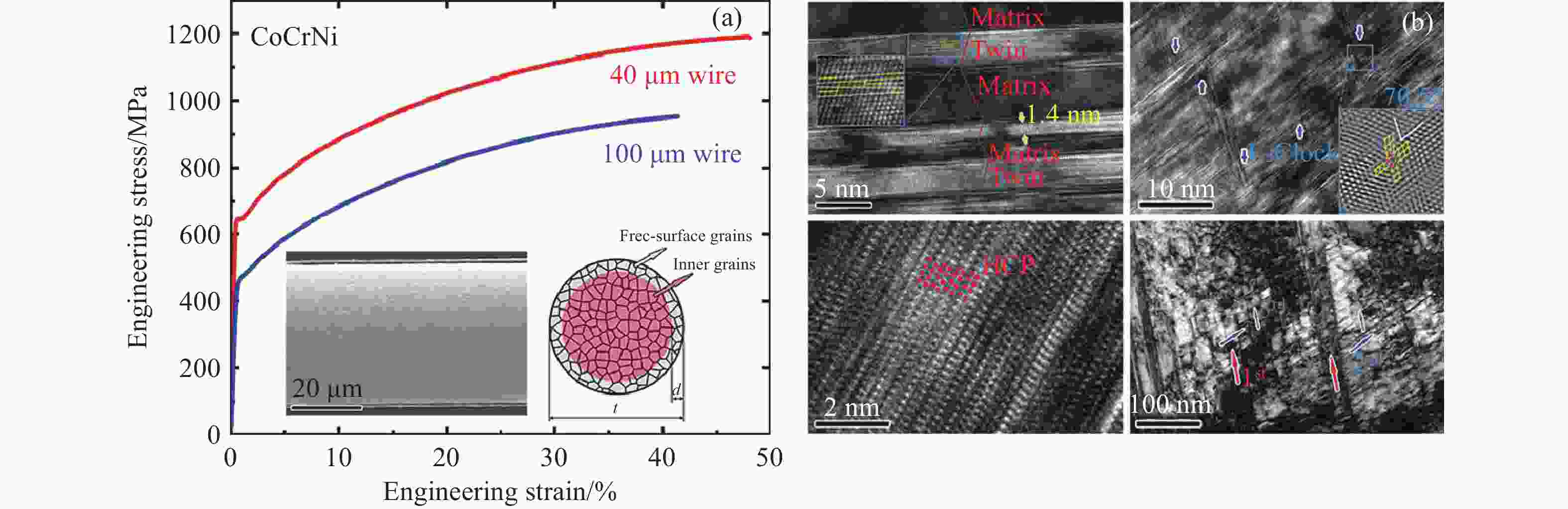
图 12 CoCrNi中熵合金纤维力学性能(a)和变形机理(b)[21]
-
[1] George E P, Raabe D, Ritchie R O. High-entropy alloys. Nat Rev Mater, 2019, 4(8): 515 doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0121-4 [2] Li W D, Xie D, Li D Y, et al. Mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2021, 118: Art No. 100777 [3] Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001 [4] Lu Y P, Dong Y, Guo S, et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: Eutectic high-entropy alloys. Scientific reports, 2014, 4: Art No. 6200 [5] Ye Y F, Wang Q, Lu J, et al. High-entropy alloy: Challenges and prospects. Mater Today, 2016, 19(6): 349 doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.026 [6] Li Z M, Raabe D. Strong and ductile non-equiatomic high-entropy alloys: Design, processing, microstructure, and mechanical properties. JOM, 2017, 69(11): 2099 doi: 10.1007/s11837-017-2540-2 [7] Gao M C, Miracle D B, Maurice D, et al. High-entropy functional materials. J Mater Res, 2018, 33: 3138 doi: 10.1557/jmr.2018.323 [8] Li Z Z, Zhao S T, Ritchie R O, et al. Mechanical properties of high-entropy alloys with emphasis on face-centered cubic alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2019, 102: 296 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.12.003 [9] Lu Z P, Wang H, Chen M W. et al. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics, 2015, 66: 67 [10] Shi P J, Ren W L, Zheng T X, et al. Enhanced strength–ductility synergy in ultrafine-grained eutectic high-entropy alloys by inheriting microstructural lamellae. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 489 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08460-2 [11] Pan Q S, Zhang L X, Feng R, et al. Gradient cell–structured high-entropy alloy with exceptional strength and ductility. Science, 2021, 374(6570): 984 doi: 10.1126/science.abj8114 [12] Xu X D, Liu P, Hirata A, et al. Microstructural origins for a strong and ductile Al0.1CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy with ultrafine grains. Materialia, 2018, 4: 395 doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2018.10.015 [13] Lei Z F, Liu X J, Wu Y, et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature, 2018, 563: 546 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0685-y [14] Yang T, Zhao Y L, Luan J H, et al. Nanoparticles-strengthened high-entropy alloys for cryogenic applications showing an exceptional strength-ductility synergy. Scripta Mater, 2019, 164: 30 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2019.01.034 [15] Sohn S S, da Silva A K, Ikeda Y, et al. Ultrastrong medium-entropy single-phase alloys designed via severe lattice distortion. Adv Mater, 2018, 31(8): Art No. 1807142 [16] He B B, Hu B, Yen H W, et al. High dislocation density-induced large ductility in deformed and partitioned steels. Science, 2017, 357(6355): 1029 doi: 10.1126/science.aan0177 [17] Lv R, Shi Y Z, Dai S, et al. Strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy via coupling partial recrystallization and hierarchical precipitation. Mater Sci Eng A, 2024, 889: Art No. 145827 [18] Li R, Liu X J, Liu W H, et al. Design of hierarchical porosity via manipulating chemical and microstructural complexities in high-entropy alloys for efficient water electrolysis. Adv Sci, 2022, 9(12): Art No. 2105808 [19] Li D Y, Li C X, Feng T, et al. High-entropy Al0.3CoCrFeNi alloy fibers with high tensile strength and ductility at ambient and cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater, 2017, 123: 285 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.10.038 [20] Kwon Y J, Won J W, Park S H, et al. Ultrahigh-strength cocrfemnni high-entropy alloy wire rod with excellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement. Mater Sci Eng A, 2018, 732: 105 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.06.086 [21] Chen J X, Chen Y, Liu J P, et al. Anomalous size effect in micron-scale cocrni medium-entropy alloy wire. Scripta Mater, 2021, 199: Art No. 113897 [22] Kao Y F, Chen S K, Chen T J, et al. Electrical, magnetic, and hall properties of Al x CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509(5): 1607 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.10.210 [23] Zhang L J, Yu P F, Cheng H, et al. Nanoindentation creep behavior of an Al0.3CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Metall Mater Trans A, 2016, 47(12): 5871 doi: 10.1007/s11661-016-3469-8 [24] Zhao Y Y, Li H, Wang Y S, et al. Shape memory and superelasticity in amorphous/nanocrystalline Cu-15.0 atomic percent (at.%) Sn wires. Adv Eng Mater, 2014, 16(1): 40 doi: 10.1002/adem.201300167 [25] Zeller S, Gnauk J. Shape memory behaviour of Cu–Al wires produced by horizontal in-rotating-liquid-spinning. Mater Sci Eng A, 2008, 481/482: 562 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.12.200 [26] Glock S, Zhang X X, Kucza N J, et al. Structural, physical and damping properties of melt-spun Ni–Mn–Ga wire-epoxy composites. Composites Part A, 2014, 63: 68 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.04.005 [27] Ochin P, Dezellus A, Plaindoux P, et al. Shape memory thin round wires produced by the in rotating water melt-spinning technique. Acta Mater, 2006, 54(7): 1877 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.12.013 [28] Zhao S, Seitz J M, Eifler R, et al. Zn–Li alloy after extrusion and drawing: Structural, mechanical characterization, and biodegradation in abdominal aorta of rat. Mater Sci Eng C, 2017, 76: 301 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.02.167 [29] Peng Q M, Fu H, Pang J L, et al. Preparation, mechanical and degradation properties of Mg–Y-based microwire. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2014, 29: 375 doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.09.015 [30] Xu X, Mi G Y, Luo Y Q, et al. Morphologies, microstructures, and mechanical properties of samples produced using laser metal deposition with 316L stainless steel wire. Opt Laser Eng, 2017, 94: 1 [31] Benedetti I, Gulizzi V, Mallardo V. A grain boundary formulation for crystal plasticity. Int J Plast, 2016, 83: 202 doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2016.04.010 [32] Zhou S C, Dai C D, Hou H X, et al. A remarkable toughening high-entropy-alloy wire with a bionic bamboo fiber heterogeneous structure. Scripta Mater, 2023, 226: Art No. 115234 [33] Huo W Y, Fang F, Zhou H, et al. Remarkable strength of CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy wires at cryogenic and elevated temperatures. Scripta Mater, 2017, 141: 125 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.08.006 -



 下载:
下载: